Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Chronic Achilles Tendonitis, ESWT for Achilles Tendonitis or Tendinitis, Pittsburgh PA
Achilles Tendonitis
An Overview
Suffix “itis” refers to inflamed, in this case used when fibers of a tendon gets torn, they get inflamed. Acute tendonitis is sudden inflammation, within few days, and is usually due to an overloading strain during a specific exercise movement, misstep or fall. Symptoms include but not limited to pain abruptly following a strain. Sharp pain at activity onset, can decrease in intensity your exercise progresses. The most significant pain is when jumping or pushing off. Stiffness in the morning, pain may return after exercise or longer periods of inactivity. Pain usually subsides when the ample rest is allowed, and may feel better with cold compression.

Some chronic Achilles tendonitis causes include:
- Untreated Acute Achilles tendonitis – inflexible or weak calves or tendons, with scar tissue (soleus or gastrocnemius)
- Not stretching or warming up before exercise.
- Wearing poor supporting shoes, such as high heels, this causes calf muscles to contract, thus providing little tendon slack
- Uneven or a change in terrain (hills) but trying to build up stabilizer muscles with training on actual uneven surfaces can also help remedy.
- High arches, fallen arches or pes planus (also called flat feet) causes stress on the Achilles tendon.
- Sometimes caused by arthritis, bony growths on the heel, can irritate the tendon.
- Some causes are improper before and after warm-ups, including stretching when doing jumping or running exercises.
- Previous achilles tears may leave scar tissue and a training regimen to build up inflexible or weak calf muscles.
- Try out shoes for half hour at a time to break them in, avoid sudden footwear changes, poor running shoes or high heels.
What is extracorporeal shock wave therapy and how does it work?
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy, also referred to as ESWT, is a nonsurgical method that delivers high-energy acoustic (sound) waves to a targeted area in order to to treat various musculoskeletal conditions, including achilles tendonitis. ESWT works in 3 ways:
- Desensitization. Local anesthesia is administered prior to the procedure. However, the ESWT is a very powerful machine, and the targeted area will become increasingly desensitized throughout the procedure.
- It changes a chronic injury into an acute injury. Chronic injuries occur from overuse of an area of the body over an extended period of time. Achilles tendonitis is an example of chronic injury.
- Vascularization. During the ESWT procedure, microscopic and controlled injuries are induced. These injuries “jump start” the overall healing process by promoting the growth of new blood vessels in the achilles tendon (vascularization), and giving your body the tools that it needs to heal itself naturally.
Benefits of ESWT vs. Surgery
ESWT is a non-invasive procedure requiring only local anesthesia to the targeted treatment area.
Surgery is an invasive procedure where you will need to be placed completely under general anesthesia.
ESWT has little to no downtime, other than not participating in overly strenuous activities for 2 months following the procedure.
Following achilles tendonitis surgery, patients will be required to wear a protective boot and/or use crutches. The healing time following surgery is a minimum of 6 months.
Physical therapy is not needed following the ESWT for achilles tendonitis
Several months of physical therapy is often required and needed following surgical correction.
While ESWT is not covered by most insurance companies, it is cost effective.
Surgical procedures can be very expensive, especially if a patient has a high deductible or poor health care coverage.
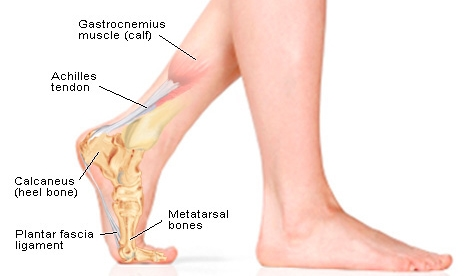
Achilles tendon
The Achilles tendon is a band of tough, fibrous tissue found in the posterior ankle between a person’s calf muscle (gastrocnemius) and heel bone (calcareous). The Achilles tendon, sometimes referred to as the “heel cord,” is the strongest tendon in the human body, yet it is often the site of chronic and debilitating injury.
Function of the Achilles tendon
The function of the Achilles tendon is to allow the foot to bend. Injury to the Achilles tendon may prevent a person from being able to walk or stand, as the Achilles tendon is the main reinforcement in the ankle, holding the ankle in place.
Is it advisable to continue exercising or participating in sports with Achilles tendonitis, or should physical activities be paused entirely?
Whether you should continue exercising or participating in sports with Achilles tendonitis depends on the severity of your condition and the advice of your healthcare provider. Here are some general guidelines:
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: It’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider, such as a sports medicine doctor or a physiotherapist, for an accurate diagnosis and personalized advice. They can assess the severity of your Achilles tendonitis and recommend an appropriate course of action.
- Rest and Modification: In most cases, rest is necessary to allow the inflamed Achilles tendon to heal. Your healthcare provider might recommend temporarily pausing activities that put stress on the tendon, such as running or jumping. They may also suggest modifying your exercise routine to avoid aggravating the condition.
- Low-Impact Activities: Depending on your condition, your healthcare provider might encourage low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling, which put less strain on the Achilles tendon. These activities can help maintain your overall fitness level while allowing the tendon to heal.
Is physical therapy beneficial for individuals with Achilles tendonitis, and what exercises are commonly recommended?
Yes, physical therapy can be highly beneficial for individuals with Achilles tendonitis. A physical therapist can design a tailored exercise program to strengthen the Achilles tendon, improve flexibility, and promote healing. Here are some common exercises that might be recommended:
- Eccentric Heel Drops: Standing on a step or raised surface, rise onto your toes (plantarflexion) and then lower your heels below the step (dorsiflexion) in a slow, controlled manner. This eccentric contraction can help strengthen the Achilles tendon.
- Calf Stretches: Gently stretch your calf muscles, as tight calf muscles can contribute to Achilles tendonitis. Various stretches, such as the wall stretch or towel stretch, can be effective.
Chronic Achilles tendonitis
Chronic Achilles tendonitis is one of the most common injuries to the Achilles tendon, occurring in 6 out of 100 inactive people and even higher in those who are active. Chronic Achilles tendonitis occurs from overuse, it may even be acute tendonitis left untreated or never been allowed sufficient rest, which results in inflammation from microtraumas in the tendon. These microtraumas happen over an extended period of time, which classifies this type of injury as chronic, rather than acute (a sudden, traumatic injury). Its common the tendon becomes inflexible and enlarged as scar tissue builds up.
Symptoms of Chronic Achilles tendonitis
Common symptoms of chronic Achilles tendonitis include:
- Foot Pain that occurs gradually, rather than suddenly
- Inflammation, which may be seen as a lump 2cm above the heel
- Pain while exercising
- Pain while performing daily activities, such as walking or standing
- Pain that increases while walking uphill or jumping
- Pain or stiffness that occurs after 30 minutes or more of rest
- Warm and tender to the touch
- Swollen or thicker Achilles tendon
- Most significant pain is when jumping or pushing off
If you hear a “pop” sound, feel a sharp pain in the back of the ankle, and it becomes difficult to walk or move your ankle – your Achilles tendon has possibly ruptured.
Chronic Achilles tendonitis treatment NYC
Treatments for Achilles tendonitis include:
- Resting and/or immobilizing the tendon
- Applying ice to the area to control inflammation and pain
- Exercises specifically designed to strengthen the Achilles tendon
- Wearing heel lifts in the shoes to relieve tension to the tendon
- Wearing orthotics in the shoes for support and protection
- Night splinting
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Injection or a non-cortisone, anti-inflammatory solution, into the tendon
- Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT)
- Surgery, although not recommended as this is an invasive procedure
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know that I have Achilles tendonitis in Youngstown?
Achilles tendonitis is diagnosed by a podiatrist specializing in foot and ankle injuries. A podiatrist can typically diagnosis Achilles tendonitis in Youngstown by:
- Pain or swelling in your heel
- Warmth in your tendon and heels
- Difficulty in walking or standing for long periods
- Discomfort behind your calf, especially when you walk or touch it
- Thickening of your tendons
- Stiffness in your heel
What Are Risk Factors Of Achilles Tendonitis?
Every single person in this world can develop achilles tendonitis, it doesn’t matter who you are, you won’t be safe from this problem.
However, there are some factors that can make you more likely to get achilles tendonitis, here are some risk factors of it:
- Having weak or tight muscles
- You have suddenly tried a new sport
- Being overweight, excess weight puts pressure on your legs
- Suffering from plantar fasciitis or heel spurs
- Being a men
- Being over the age of 30
- Wearing uncomfortable shoes, this can include tight shoes or shoes that don’t provide enough space
- Performing intense exercises
- Landing or working on hard surfaces like concrete
How To Prevent Achilles Tendonitis In Future?
Completely preventing achilles tendonitis isn’t possible however you can try to prevent it’s symptoms and decrease the risks.
Here are some of the most useful tips to prevent achilles tendonitis:
- Before any kind of activity or exercise properly warm up and stretch your muscles. This will help your muscles to avoid injuries and work properly
- If you are going to start a new exercises then you should start slowly, do not force yourself and go easy on yourself
- Avoid high heels, they can cause many foot and heel problems like plantar fasciitis and achilles tendonitis.
- Avoid working and performing exercises on hard surfaces, if your work requires working on hard surfaces then choose shoes with a lot of cushioning
- If you feel pain while doing any kind of activity then immediately stop it
- If you feel pain in heel then apply ice and reduce pain, if it still doesn’t go away then look for medical treatment.
Do I need to have X-rays taken to diagnosis Achilles tendonitis in Philadelphia?
Diagnostic imaging, such as X-ray, is not typically needed in order for a podiatrist to diagnose Achilles tendonitis in Philadelphia. However, ultrasound imaging and MRI may be used if a diagnosis of Achilles tendonitis is not clear.
Is surgery a common treatment option for severe cases of Achilles tendonitis?
Surgery is generally considered a treatment option for severe cases of Achilles tendonitis when conservative measures have not been successful or if there is significant tendon damage. Surgical interventions may include:
- Debridement: Removal of damaged tissue or bone spurs.
- Tendon Repair: Suturing or reattaching the torn or damaged tendon.
- Tendon Transfer: Using a nearby tendon to replace the damaged portion of the Achilles.
- Lengthening: Addressing a tight Achilles tendon that contributes to the condition.
Can certain sports or activities increase the risk of Achilles tendonitis?
Yes, certain sports and activities that involve repetitive stress on the Achilles tendon or sudden, intense movements can increase the risk of Achilles tendonitis. These activities include:
- Running and Jogging: Long-distance running or sudden increases in running intensity.
- Basketball: Jumping and sudden stops or changes in direction.
- Tennis or Racquet Sports: Quick lateral movements and frequent stops.
- Soccer: Running, cutting, and pivoting during play.
- Gymnastics: Repetitive jumping and landing on hard surfaces.
- Dancing: Particularly styles that involve frequent jumping or high-impact movements.
- Track and Field Events: Especially those that involve jumping or sprinting.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Intense bursts of activity and sudden movements.
Is surgery a common treatment option for severe cases of Achilles tendonitis?
Surgery is not the first-line treatment for Achilles tendonitis. Conservative approaches are typically attempted first, and surgery is considered when non-surgical methods have been ineffective, or if there is severe damage to the Achilles tendon. Common conservative treatments include rest, physical therapy, orthotic devices, and anti-inflammatory medications.
Surgery for Achilles tendonitis may involve procedures such as debridement (removal of damaged tissue), tendon repair, or tendon transfer. The decision for surgery depends on factors like the severity of the condition, response to conservative treatments, and the individual’s overall health.
How can I treat Achilles tendonitis in Chicago?
There are several options for treatment of Achilles tendonitis in Chicago. Conservative treatments, such as strengthening exercises, stretching, icing, resting, and wearing heel lifts and/or orthotics should become part of your daily routine in order to heal and prevent further injury to the Achilles tendon. Non-cortisone anti-inflammatory medications may also be injected into the Achilles tendon to help reduce inflammation. Cortisone injections may weaken the tendon and cause a rupture, so they are often not recommended, especially for active individuals. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy, or simply ESWT, in Chicago is a very effective, non-surgical option to treat chronic Achilles tendonitis.
What are the potential complications if Achilles tendonitis is not addressed promptly?
If Achilles tendonitis is not addressed promptly, several potential complications can arise, affecting both the tendon and overall foot function. These complications may include:
- Tendinosis: Chronic inflammation and strain on the Achilles tendon can lead to degeneration and changes in the tendon’s structure, known as tendinosis. This condition involves microtears in the tendon and is a more chronic and degenerative state.
- Achilles Tendon Rupture: Prolonged Achilles tendonitis, especially when associated with tendinosis, can increase the risk of a partial or complete tendon rupture. This is a severe and painful injury that often requires surgical intervention.
- Tendon Thickening: Persistent inflammation and strain may cause the Achilles tendon to thicken, leading to increased stiffness and reduced flexibility.
- Chronic Pain: Long-standing Achilles tendonitis can result in chronic pain, limiting daily activities and potentially impacting the quality of life.
- Limited Range of Motion: As the tendon undergoes structural changes, individuals may experience a decreased range of motion in the ankle joint.
What role does improper stretching or warming up play in Achilles tendonitis?
Improper stretching or inadequate warming up can contribute to the development or exacerbation of Achilles tendonitis. Here’s how:
- Insufficient Flexibility: Tight or inflexible calf muscles and Achilles tendons are more prone to strain and injury. Inadequate stretching can lead to reduced flexibility, increasing stress on the Achilles tendon during physical activities.
- Overloading the Tendon: Without proper warm-up and stretching, sudden or intense physical activity can place excessive stress on the Achilles tendon. This abrupt loading can lead to microtears, inflammation, and the development of tendonitis.
- Reduced Blood Flow: Warm-up activities, including dynamic stretching, increase blood flow to the muscles and tendons. Inadequate warm-up may result in insufficient blood flow to the Achilles tendon, impeding its ability to cope with increased demand during activity.
What should I expect during the EWST procedure in Baltimore?
When you come the closest ESWT provider in Baltimore or your area, you will be placed comfortably lying on your side. The podiatrist will administer a local anesthesia to ensure that you feel no pain while you are having the procedure. Once your heel is completely numb, your foot will be placed on the therapy head bubble and against the ultrasound transducer. A trained professional will apply a gel to your skin and use the transducer to produce an ultrasound image of your achilles tendon. This image will allow us to target the area(s) of treatment. Once located, the procedure will begin, and 3,800 pulses will be administered over the next 18 to 20 minutes. During the treatment time, you should not feel pain, but you will feel pressure and what some have described as a “light rubber band snap” on the targeted area. You will also be able to hear the shockwaves as they are being produced. The treatment starts at the lowest intensity level, which you will hear as a slow tapping from the machine, and gradually increases to “therapy level” where you will hear an increase in the tapping. We want you to be as comfortable as possible during the procedure. Please feel free to read a magazine or even take a quick nap!
How long does an ESWT procedure take?
The ESWT procedure typically takes 18-20 minutes per side, 36-40 minutes bilateral (two sides).
What should I expect following the EWST procedure in Philadelphia?
Immediately following the procedure, your local anesthesia will not yet have worn off, so we recommend that you have a driver. You may notice some bruising or tenderness at the injection site. This is completely normal, however, if you have any concerns, please contact the podiatrist office where you had the procedure or call 724-991-0116. For the next 3 months, you should not take any antiinflammatories or apply any natural anti-inflammatories, such as heat or ice to the treated area. Anti-inflammatoires will slow down the healing process that is taking place. You make take acetaminophen (Tylenol) to help with any discomfort you may be experience. It is also recommended that you not engage in any overly strenuous exercise routines, such as powerlifting, squats, or kettlebell. Your body will continue to heal over the next 6 months following the ESWT procedure. If any time you have questions or concerns, please contact the podiatrist office where you had the procedure or call 724-991-0116.
I saw an advertisement for ESWT in Pittsburgh and am wondering, what is the effectiveness of ESWT for achilles tendonitis?
In the experience of Pittsburgh podiatrists performing ESWT, there is a 92% success rate after 6 months following ESWT for achilles tendonitis. It is very unlikely that you would need to have a 2nd procedure done. Please take into account that ESWT in Pittsburgh is not a “cure all” and should not be used as the only means of healing. ESWT will give your body the tools it needs to effectively heal. However, you must help the healing process by continuing to stretch daily, icing in the evenings (after 3 months), and wearing supportive orthotics in your shoes.
I want to have ESWT in New Jersey. Will the ESWT be painful?
During the ESWT in New Jersey, or a podiatrist office near you, you should not experience any pain. The podiatrist will administer a local anesthetic to the area prior to the procedure. As the ESWT machine is very powerful, it will also desensitize the area ensuring that you have a comfortable, pain-free experience!
What makes me a good candidate for ESWT in Cincinnati?
Good considerations for ESWT include:
- A diagnosis of achilles tendonitis for 6 months or longer. If you are have not yet been diagnosed by a podiatrist or physician, please call to make an appointment at a participating podiatrist office providing ESWT closest to you 724-991-0116.
- Trying at least three conservative treatments, which have failed. Conservative treatments may include, but are not limited to, wearing plantar fasciitis arch supports in your shoes, taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen, night splinting, and cortisone injections.
What makes me a poor candidate for ESWT?
You are a good candidate for ESWT as long as you are suffering from problem like Achilles tendonitis or plantar fasciitis.
However, there are some factors that can make you a bad candidate of ESWT, which means even if you have Achilles tendonitis, your doctor won’t recommend it to you.
If you are wondering what are those factors that prevent you from getting ESWT then here are some of them:
- Suffering from chronic health conditions such as diabetes, weak immune system or low blood pressure
- Being pregnant, if you are pregnant or planning to get pregnant soon then ESWT isn’t for you
- Having excess weight isn’t allowed either, your doctors r may recommend you to lose weight before getting ESWT.
- Smokers and drinkers can’t get this treatment as well as well since both of them decreases the healing process
Recovery For ESWT
The great thing about ESWT is that it doesn’t have a long recovery process, you don’t need to spend days at hospital or home at all.
All you need is one or two week rest to properly recovery, during this time you may experience bruising and a little pain too but don’t worry since these symptoms are completely normal.
Your recovery can depend on your health and age as well, people with weak immune system may take longer to heal.
Furthermore, you can continue your daily activities after few days of treatment, but avoid vigorous activities and do not put a lot of pressure on the treated area.
After the treatment is done your doctor will provide you with some recovery tips too, make sure to follow them properly!
If you can’t deal with the pain then you should take over-the-counter pain relievers.
Lastly, if the pain doesn’t go away even after weeks then do not forget to visit your doctor.
What is the cost of ESWT in New York City?
As ESWT is no longer covered by many health insurance companies, we encourage anyone, whether you are from New York City, Baltimore, Cleveland, etc., to contact an office near you to discuss pricing and payment options. You can call 724-991-0116 for assistance in locating a podiatrist office in your area.
Is ESWT in Washington D.C. FDA approved for achilles tendonitis?
Achilles tendon ESWT in Cleveland is not FDA approved. However, ESWT is a state-of-the-art procedure that has been proven to be a very effective alternative to surgical correction for achilles tendonitis. It is FDA approved for plantar fasciitis which is very similar. Achilles ESWT is widely undertaken in Europe and is done off label in the United States on an out of pocket basis, with great success.
How do I schedule an appointment to have ESWT in Morgantown?
ESWT has been found to be a very effective alternative to surgery, please call 724-991-0116 with any questions or for assistance in scheduling and appointment for ESWT in Morgantown or another location near you!
